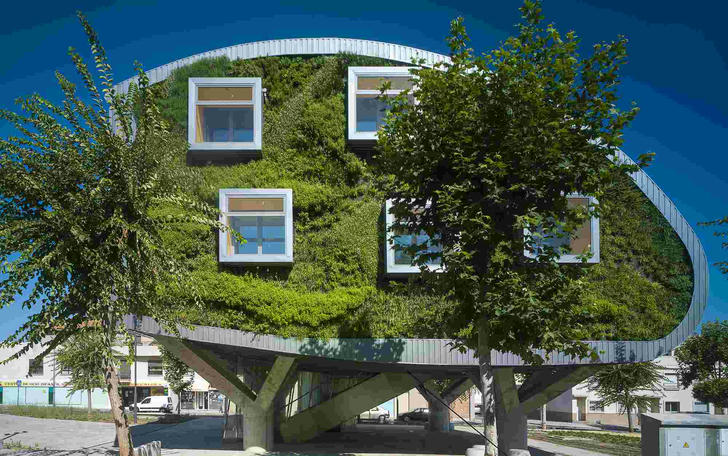
Emerging Trends in Sustainable Architecture: Innovations to Watch in 2024
As global awareness of environmental issues intensifies, the architecture industry is experiencing a shift towards more sustainable practices. In 2024, we anticipate a significant leap in innovations that aim to minimize the environmental impact of buildings, improve energy efficiency, and promote greener urban environments. This report explores the most important emerging trends in sustainable architecture that are poised to shape the industry in the coming year.

1.Adaptive Reuse and Circular Design

One of the most impactful trends in sustainable architecture is the move towards adaptive reuse and circular design. Instead of demolishing older buildings, architects are increasingly focused on transforming existing structures for new purposes, significantly reducing waste and resource consumption. Circular design, which emphasizes using materials that can be reused or recycled at the end of a building's life cycle, is becoming integral to many projects.
1.1 Benefits of Adaptive Reuse
Waste Reduction: Repurposing existing structures prevents demolition waste from ending up in landfills.
Resource Efficiency: Using existing building materials reduces the demand for new resources, lowering the environmental footprint.
Cultural Preservation: Adaptive reuse helps preserve historical buildings, fostering cultural heritage and sustainability simultaneously.
1.2 Circular Design in 2024
In the coming year, expect to see a rise in buildings designed with disassembly in mind. These structures use materials that can be easily deconstructed and repurposed, promoting a closed-loop lifecycle in architecture.
2.Net-Zero Energy Buildings
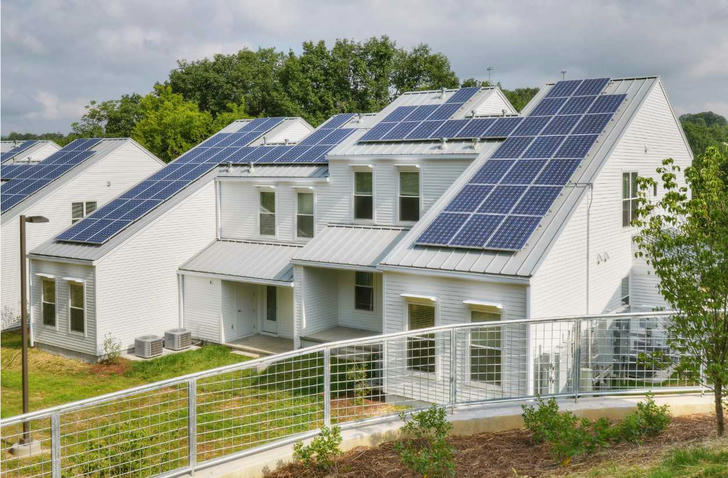

Net-zero energy buildings (NZEBs) are rapidly becoming the gold standard in sustainable architecture. These buildings are designed to produce as much energy as they consume over a year, effectively reducing or eliminating reliance on external energy sources. With increasing regulations and incentives encouraging the construction of NZEBs, 2024 will see wider adoption of this model.
2.1 Key Features of NZEBs
Energy Efficiency: Through advanced insulation, energy-efficient windows, and optimized building orientation, NZEBs minimize energy consumption.
On-Site Renewable Energy: Solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal systems are commonly integrated into NZEBs to generate renewable energy.
Smart Energy Management: Advanced energy monitoring and management systems ensure that buildings use energy efficiently and only when needed.
2.2 NZEBs in 2024
The technology supporting NZEBs will become more affordable and accessible. Innovations in energy storage, such as more efficient batteries, will enable buildings to store excess renewable energy for later use, further enhancing energy independence.
3.Biophilic Design
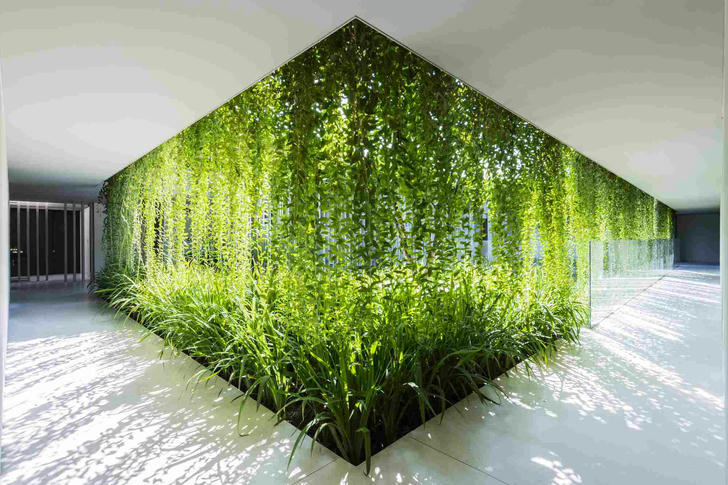

Biophilic design, which emphasizes the connection between humans and nature, is emerging as a leading trend in sustainable architecture. This approach seeks to incorporate natural elements like sunlight, vegetation, and water into building designs, enhancing both sustainability and human well-being.
3.1 The Core Principles of Biophilic Design
Natural Lighting: Maximizing daylight reduces energy use and improves occupant health and productivity.
Green Spaces: Integrating green roofs, indoor gardens, and outdoor spaces enhances biodiversity and helps reduce the urban heat island effect.
Ventilation and Air Quality: Natural ventilation strategies improve indoor air quality while reducing reliance on mechanical systems.
3.2 Biophilic Design Trends for 2024
In 2024, biophilic design will continue to evolve with a focus on sustainability. Expect to see more buildings integrating large-scale green roofs and living walls that not only beautify the space but also improve air quality and insulation.
4.3D Printing and Prefabrication
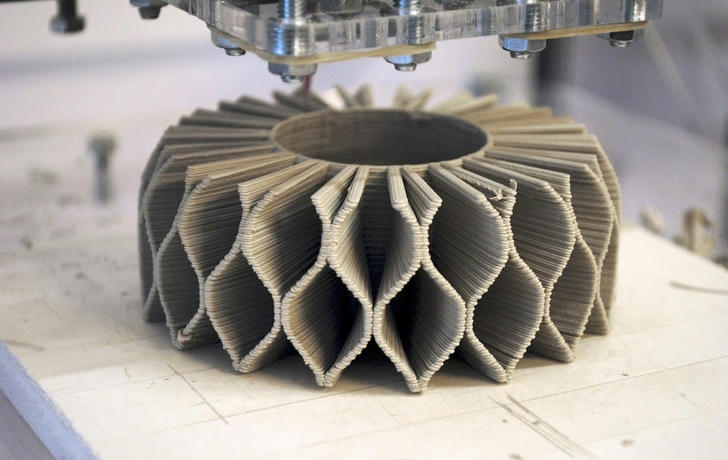
The use of 3D printing and prefabrication in architecture is accelerating the shift towards more sustainable construction practices. These technologies offer a way to reduce material waste, lower energy consumption during construction, and enhance building efficiency.
4.1 Advantages of 3D Printing
Material Efficiency: 3D printing minimizes waste by using only the materials needed to create specific components, contributing to resource conservation.
Customization: Architects can design custom, energy-efficient building components that are optimized for performance.
Reduced Transportation Emissions: With on-site 3D printing, the need to transport large quantities of materials to construction sites is minimized, reducing carbon emissions.
4.2 Prefabrication in 2024
Prefabrication is poised to become even more mainstream in 2024, particularly for sustainable housing projects. Prefabricated components are built in factories, which allows for more precise construction, less material waste, and quicker on-site assembly. Combining this with sustainable materials like cross-laminated timber (CLT) will further reduce the environmental impact of construction projects.
5.Sustainable Materials and Carbon Capture
The materials used in construction play a crucial role in a building’s sustainability profile. In 2024, we will see increased use of sustainable materials, along with innovations in carbon capture that aim to reduce the carbon footprint of buildings.
5.1 Low-Carbon and Recycled Materials
Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT): CLT is a renewable, low-carbon alternative to traditional construction materials like concrete and steel. Its use is expected to grow in 2024 due to its strength and sustainability.
Recycled Steel and Concrete: These materials reduce the need for new resource extraction and lower the overall environmental impact of construction.
Bio-Based Materials: Innovative materials like mycelium (fungus-based) and hempcrete (hemp-based concrete) are becoming viable alternatives to traditional materials, offering both sustainability and performance benefits.
5.2 Carbon Capture in Construction
Innovations in carbon capture technology are enabling buildings to absorb and store CO2, effectively turning them into carbon sinks. In 2024, expect to see more building materials, such as carbon-absorbing concrete, that actively reduce atmospheric CO2 levels.
6.Water Conservation and Management
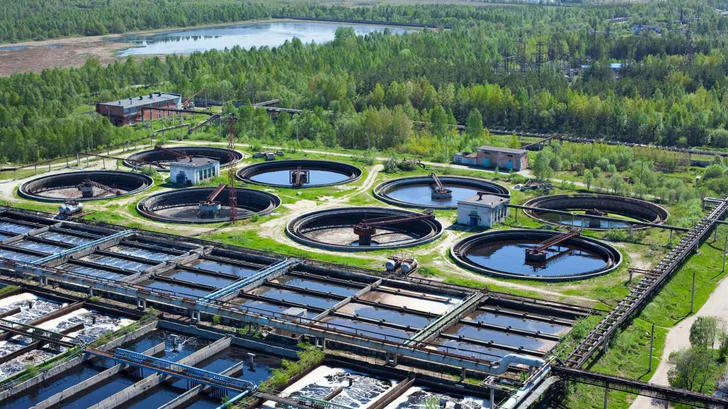

Water conservation is becoming a crucial component of sustainable architecture, especially as water scarcity becomes more pronounced in many parts of the world. Architects are increasingly integrating water-saving technologies into their designs, ensuring that buildings use water more efficiently.
6.1 Key Water Conservation Strategies
Greywater Recycling: Systems that treat and reuse greywater from sinks, showers, and washing machines are becoming more common in sustainable buildings.
Rainwater Harvesting: Collecting and storing rainwater for non-potable uses, such as irrigation and flushing toilets, helps reduce the demand on municipal water supplies.
Water-Efficient Fixtures: Installing low-flow toilets, faucets, and showerheads is a simple but effective way to reduce water consumption in buildings.
6.2 Innovations for 2024
Smart water systems, capable of monitoring and optimizing water usage in real-time, will become more widespread. These systems can detect leaks, adjust irrigation schedules based on weather conditions, and ensure that water is only used when necessary, helping to conserve this precious resource.
Conclusion
Sustainable architecture is poised for significant advancements in 2024. With innovations such as adaptive reuse, net-zero energy buildings, biophilic design, 3D printing, sustainable materials, and advanced water management systems, the architecture industry is addressing environmental challenges head-on.

